public void openDocument(String name) {
if (!canOpenDocument(name)) {
// cannot handle this document
return;
}
Document doc = doCreateDocument();
if (doc != null) {
docs.add(doc);
aboutToOpenDocument(doc);
doc.open();
doc.doRead();
}
}Template Method
Intent
Define the skeleton of an algorithm in an operation, deferring some steps to subclasses.
Template Method lets subclasses redefine certain steps of an algorithm without changing the algorithm’s structure.
Motivation
You want to support a standardized ordering or sequencing of operations within a framework, but you want subclasses to vary the execution of the steps to suit their needs
Solution
Implement template method to define an algorithm in terms of abstract operations that subclasses override to provide concrete behavior
Template Method Pattern
Hook and template methods are the building blocks of software frameworks.
They allow the implementation of commonality and variability.
Template Method
A template method defines the skeleton of an algorithm, deferring some steps to subclasses.
Subclasses can redefine some steps without changing the algorithm’s structure.
Template Method Example
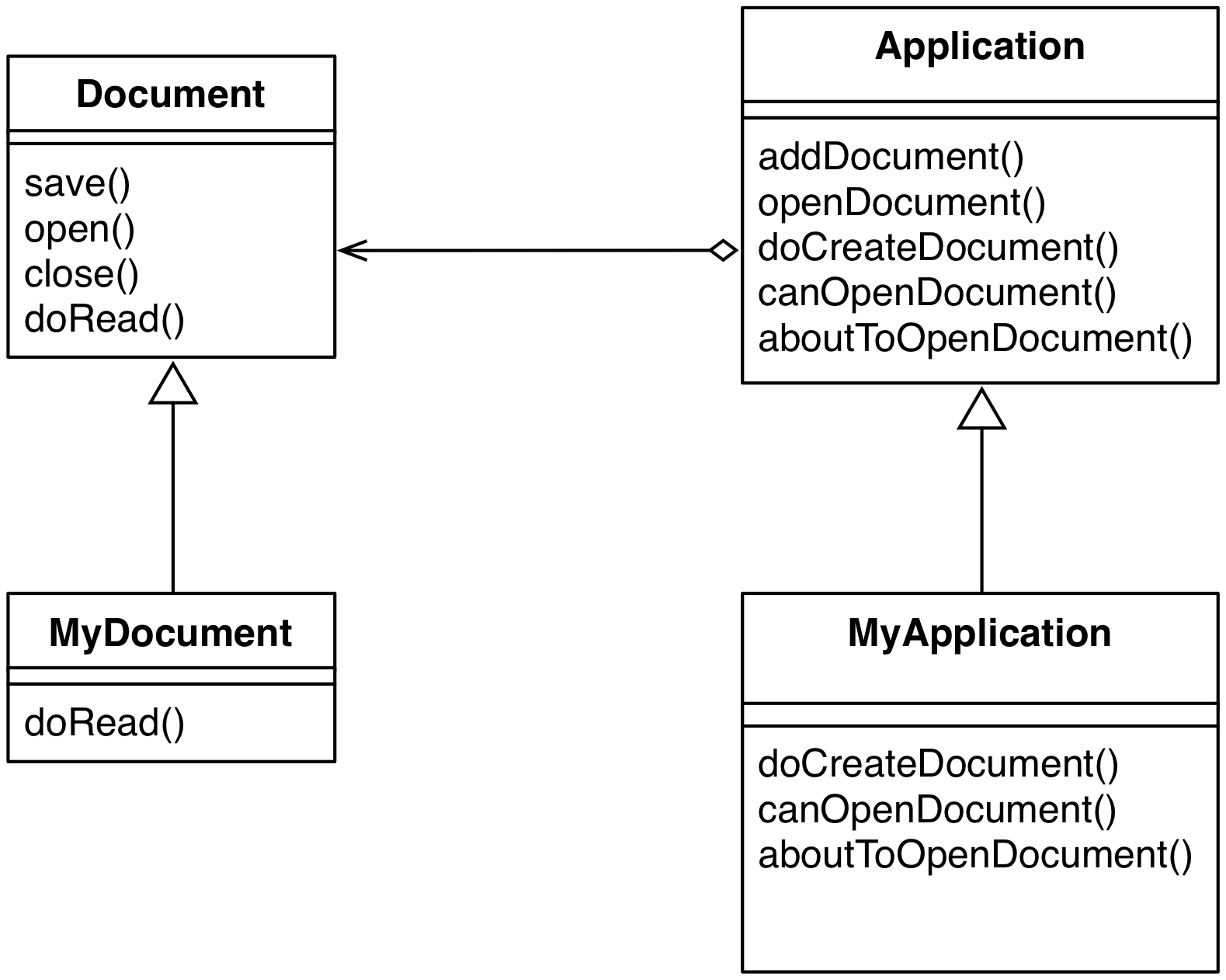
Template Method Behavior
concrete Client operations.
concrete AbstractClass operations (i.e., operations that are generally useful to subclasses).
concrete operations..
abstract operations.
factory methods (see Factory Method Pattern).
hook operations, which provide default behavior that subclasses can extend if necessary. A hook operation often does nothing by default.
Hook Methods
A hook method represents a point of variability by providing the calling interface to a variable behavior.
Each implementation of a hook method provides a variant of that behavior.
Structure
public abstract class AbstractClass {}
public void templateMethod(){
hook1();
hook2();
}
protected void hook1();
protected void hook2();
}Implementation Tradeoffs
Minimizing primitive operations
The more operations that need overriding, the more tedious things get for clients
Naming conventions: add a prefix to the names of hook methods.
The MacApp framework for prefixes template method names with "Do-": "DoCreateDocument", "DoRead", etc.
Authors and Date
Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software. Erich Gamma, Richard Helm,Ralph Johnson, and John Vlissides. Addison Wesley. October 1994.